All Categories
Featured
2 individuals acquisition joint annuities, which provide a guaranteed revenue stream for the rest of their lives. If an annuitant passes away throughout the distribution period, the remaining funds in the annuity may be handed down to a designated recipient. The certain options and tax obligation ramifications will certainly depend upon the annuity contract terms and appropriate legislations. When an annuitant passes away, the rate of interest earned on the annuity is managed differently depending upon the kind of annuity. For the most part, with a fixed-period or joint-survivor annuity, the rate of interest remains to be paid to the surviving beneficiaries. A survivor benefit is an attribute that makes sure a payment to the annuitant's recipient if they die before the annuity repayments are tired. The schedule and terms of the fatality advantage might differ depending on the particular annuity contract. A kind of annuity that quits all settlements upon the annuitant's death is a life-only annuity. Understanding the conditions of the fatality benefit prior to buying a variable annuity. Annuities go through tax obligations upon the annuitant's death. The tax obligation treatment depends upon whether the annuity is held in a qualified or non-qualified account. The funds undergo revenue tax obligation in a qualified account, such as a 401(k )or individual retirement account. Inheritance of a nonqualified annuity usually causes taxation only on the gains, not the whole amount.
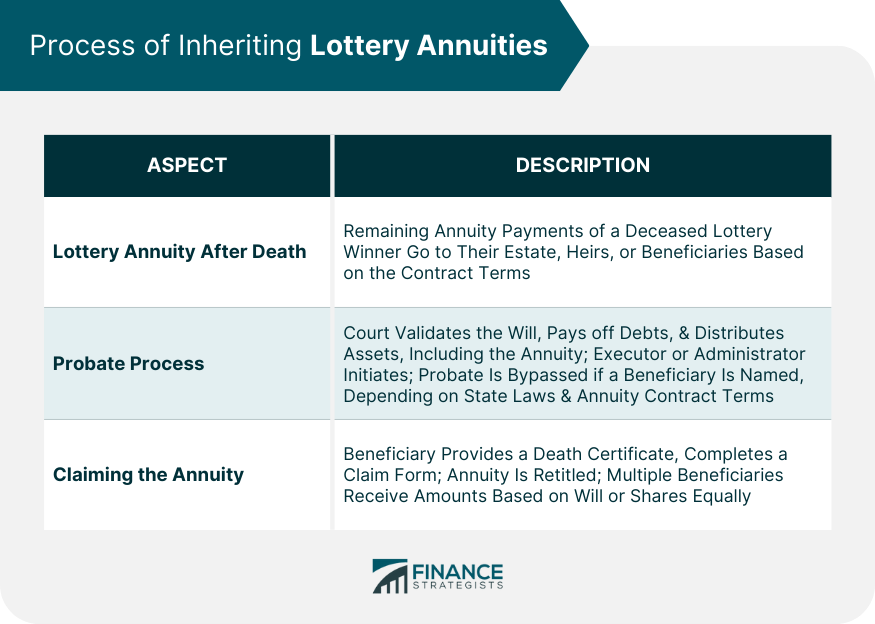
If an annuity's assigned recipient passes away, the outcome depends on the particular terms of the annuity contract. If no such beneficiaries are marked or if they, too
have passed have actually, the annuity's benefits typically revert commonly change annuity owner's proprietor. If a recipient is not called for annuity benefits, the annuity proceeds usually go to the annuitant's estate. Deferred annuities.
Taxes on inherited Lifetime Annuities payouts
Whatever part of the annuity's principal was not currently strained and any kind of earnings the annuity gathered are taxed as income for the beneficiary. If you inherit a non-qualified annuity, you will just owe taxes on the incomes of the annuity, not the principal utilized to buy it. Since you're getting the whole annuity at when, you have to pay tax obligations on the whole annuity in that tax obligation year.
Latest Posts
Understanding Financial Strategies Key Insights on Your Financial Future Defining the Right Financial Strategy Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Why Immediate Fi
Decoding How Investment Plans Work A Closer Look at What Is A Variable Annuity Vs A Fixed Annuity Breaking Down the Basics of Variable Vs Fixed Annuity Pros and Cons of Annuities Variable Vs Fixed Why
Breaking Down Your Investment Choices Everything You Need to Know About Annuity Fixed Vs Variable What Is the Best Retirement Option? Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Retirement Plans Why Var
More
Latest Posts